Adolf Müller (1884-1945), Von der Pike Auf, Zum 60. Geburtstag unseres Chefs herrn Adolf Müller zusammengestellt [Munich: H. Schwaiger, 1944]. Frontispiece portrait and approximately 300 black & white photographs on 104 glossy photo paper. 160 unnumbered leaves of text, all printed on coated glossy paper. Graphic Arts Collection 2018- in process.
Adolf Müller (1884-1945), Von der Pike Auf, Zum 60. Geburtstag unseres Chefs herrn Adolf Müller zusammengestellt [Munich: H. Schwaiger, 1944]. Frontispiece portrait and approximately 300 black & white photographs on 104 glossy photo paper. 160 unnumbered leaves of text, all printed on coated glossy paper. Graphic Arts Collection 2018- in process.
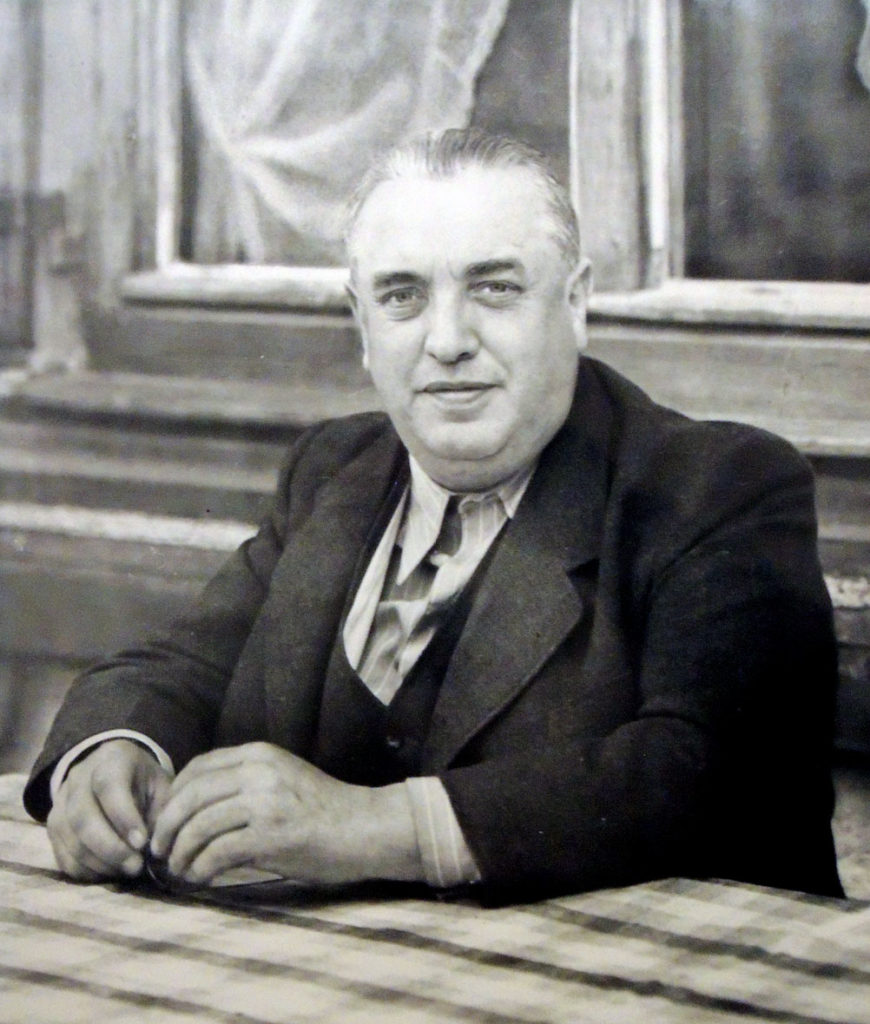
The Graphic Arts Collection recently acquired this richly illustrated festschrift for Adolf Müller (1884-1945), the publisher of Mein Kampf and close confidante of Hitler from the earliest days of the Nazi party. Issued to celebrate the publisher’s 60th birthday on May 4, 1944, only two copies were privately printed. Approximately one year later, on May 23, 1945, Müller hanged himself in prison following his capture by American troops.
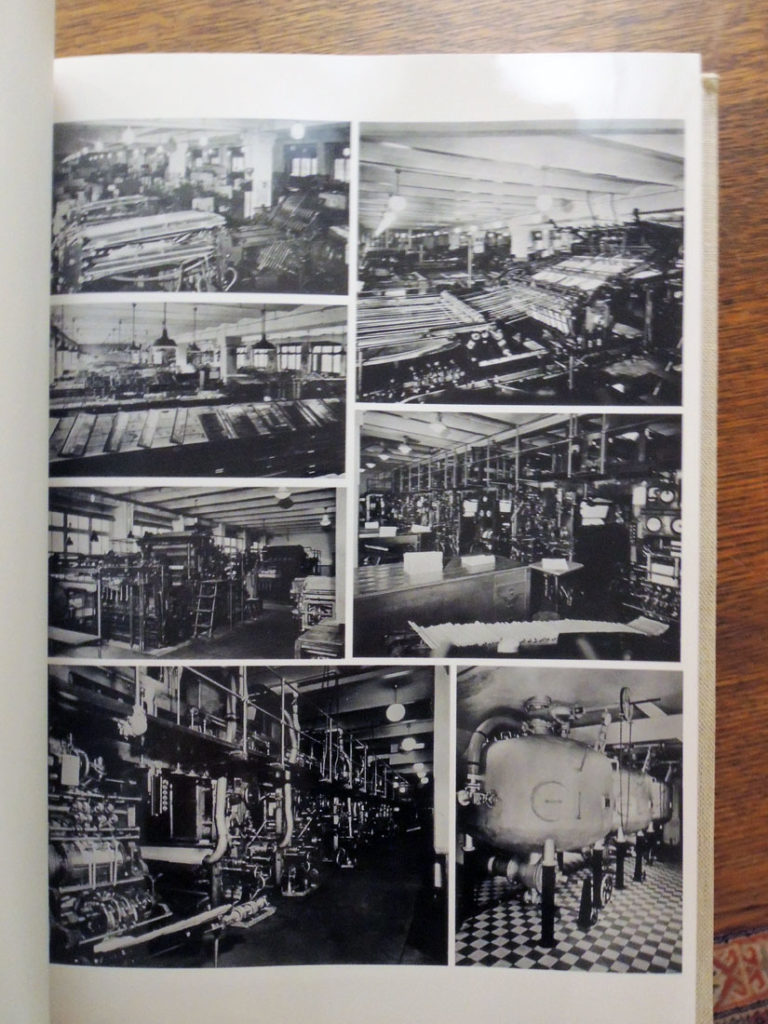
Müller’s personal copy was bound and presented to him from the firm. This is the copy now at Princeton University Library. The volume contains a first-hand history of the Nazi party’s control of media in the pre-World War II period, as well as documentation of Müller’s publishing empire and his relationship with Hitler. The photographs show printing equipment, offices and factories, intimate shots of Müller’s offices, and reproductions of significant publications.
Quotes below are from the dealer’s well-researched description:

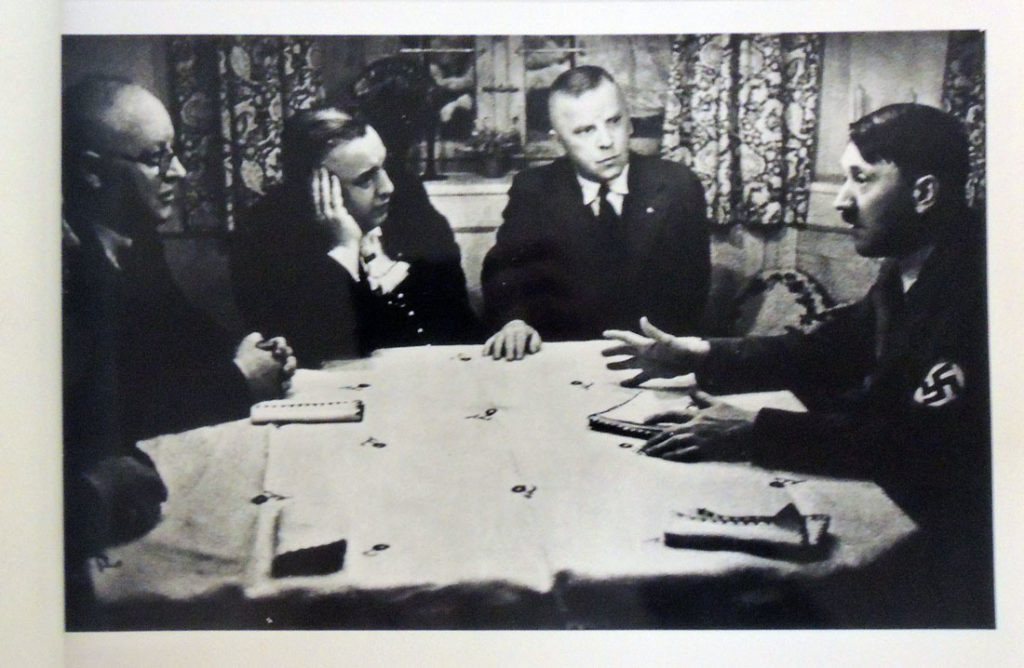
Müller was an intimate friend of Hitler — it was Müller who picked him up from Landsberg prison (documented within) in 1924 and Hitler lived in the publisher’s house in Tegernsee. Müller published Mein Kampf in 1925 and all its subsequent editions. The chief publisher of the Nazi party, he directed the printing of the newspaper “Völkischer Beobachter,” a vital arm of the Nazi propaganda effort.
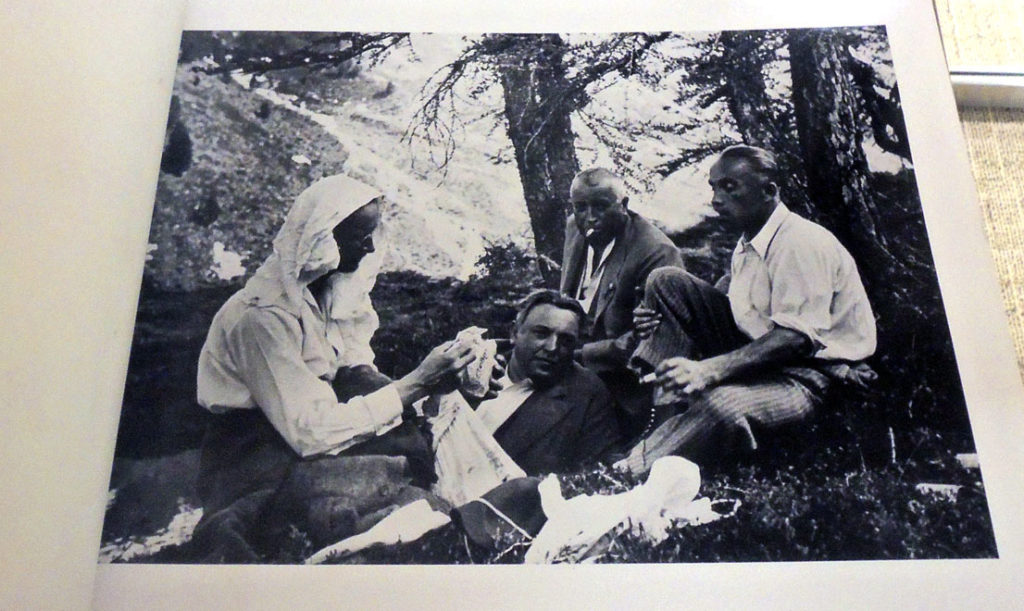
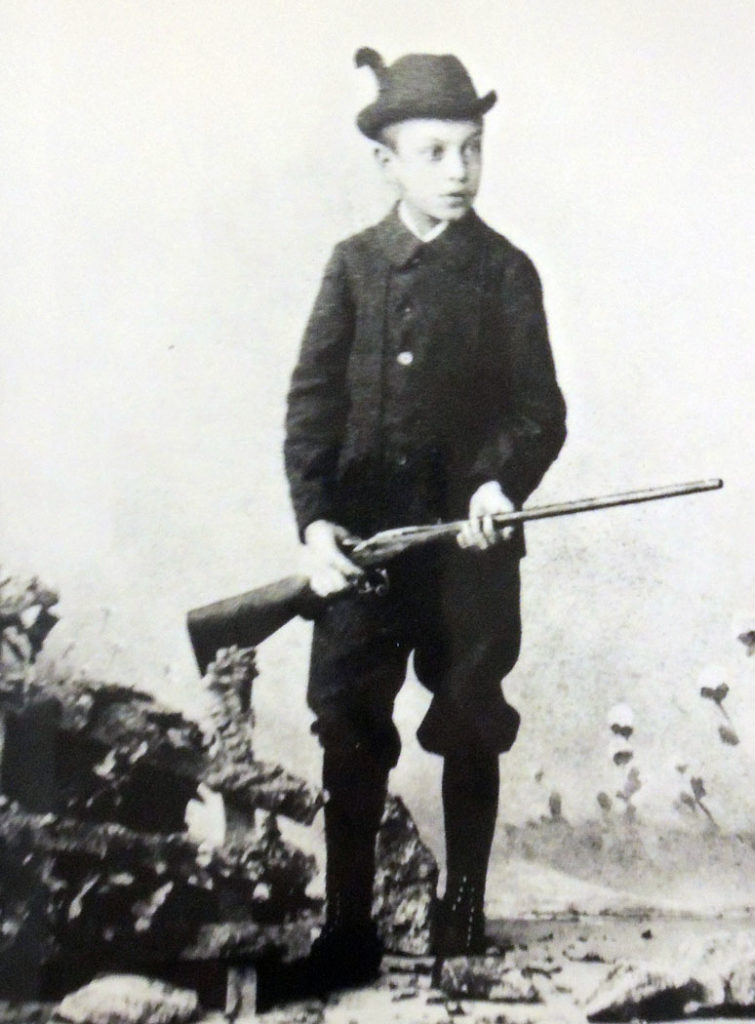
Müller parlayed his firm’s importance to the Nazi cause from its earliest days into powerful administrative positions and a close friendship with Hitler. Intimate scenes of Müller show him hunting and fishing, participating in Nazi rallies, working at his desk, conferring with prominent Nazi officials, etc. Among the many images of Müller’s personal life, Hitler appears in twelve images, including one where he has just been released from Landsberg prison following the Beer Hall Putsch and stands next to Müller’s car.
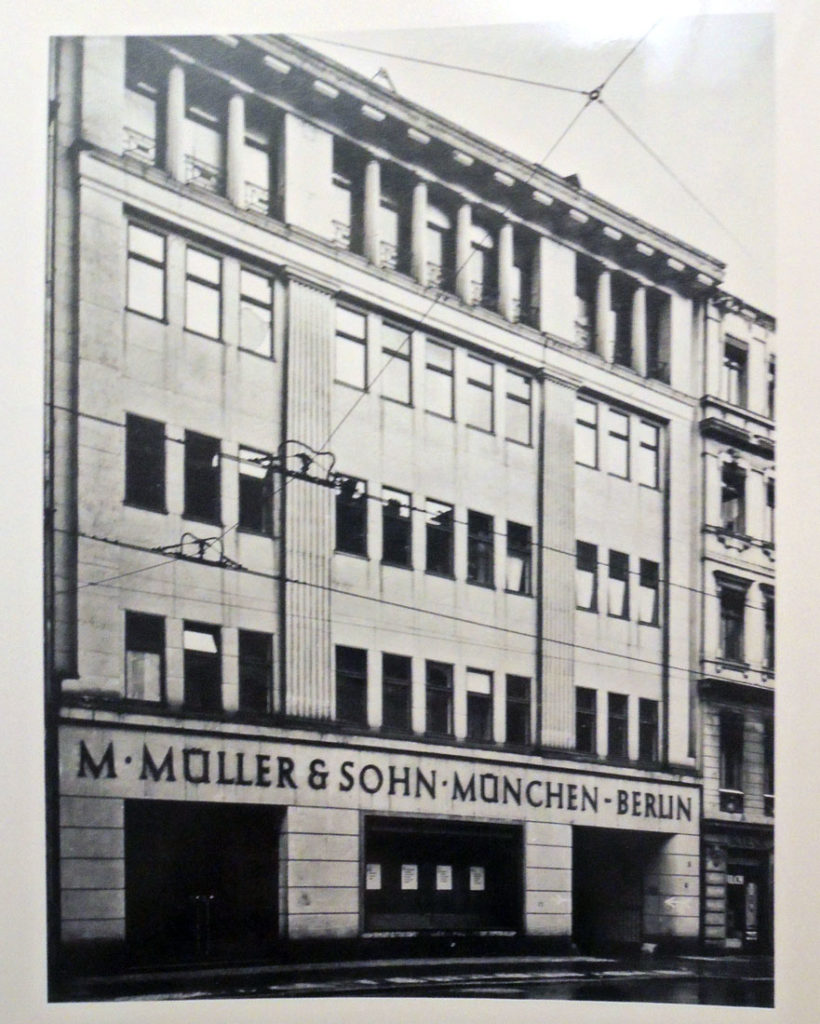
After his discharge from the German army in 1915, Müller founded the printing company Münchner Buchgewerbhaus M. Müller & Sohn, to publish newspapers and magazines. By the early 1920s he had formed friendships with members of the National Socialist German Workers’ Party and, starting in 1925, Müller’s firm was the party’s central publishing house.
Subsequently, the Nazi party entrusted to Müller the publication of Mein Kampf because of his friendship with Hitler. Once the Nazi party had taken over the German government, Müller’s business, benefitting from a near monopoly, grew exponentially. He officially joined the party at Hitler’s request in 1934. His firm printed more than two million copies weekly of various Nazi magazines and newspapers at the beginning of World War II. Müller’s leadership was an irreplaceable component of the Nazi party’s propaganda apparatus in the 1920s and through to the end of the war.

The text of this book provides a thorough account of Müller’s career, which, at times, is surprisingly candid. Certain portions touch upon the company’s claims that it was an impartial entity, even though it underwent a rapid change from a neutral publishing house into a company wholly involved in National Socialist propaganda.
Additionally, it becomes clear that this document was not intended for widespread publication since it openly discusses the company’s internal operations and political decisions in a very forthright and revealing manner.
Another section describes the firm’s entanglement in a controversy regarding the reporting of Germany’s annexation of Austria. Finally, there are extensive histories of the publication of Mein Kampf and the “Völkischer Beobachter.”
According to the preface composed by Heinrich Schwaiger, chief manager of the Munich headquarters, two copies of the work were printed, however the present copy was the only one bound and the second, which remained in sheets, can no longer be located. Despite Nazi Germany’s growing number of defeats by 1944 and the destruction of the company’s headquarters in a bombing raid, no expense was spared in this book’s production. An original Gothic font was cast especially for this book, and the company’s plant prioritized the high-quality illustrations on fine coated photo paper.


 All of the photographs are fully described and the individuals identified. Here is one example of the many indexes through the volume.
All of the photographs are fully described and the individuals identified. Here is one example of the many indexes through the volume.