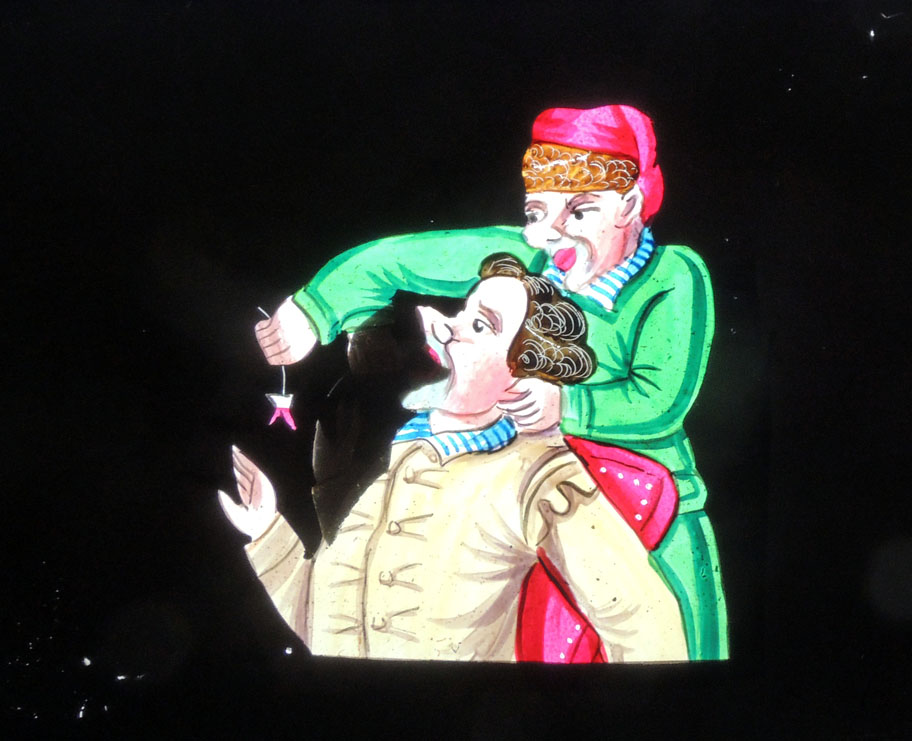
During the conservation of our circus broadsides, a large group of circus magazines and multi-page advertising were separated from the flat paper. These are now begin catalogued and housed with our other bound material. They announce many thrilling attractions from P.T. Barnum and other entrepreneurs, but one that especially caught our eye was an advertisement for Professor Faber’s “Talking Machine.”
In 1844, several American newspapers mention the first visit of Joseph Faber (ca.1800-1850) to the United States with his contraption named Euphonia:
“The Talking Machine. Having seen in one or two papers an account of this new invention we went with a friend yesterday to see it. –Mr. Faber, the artist, speaks only German, yet he has taught his machine to speak English, and speak it too better than German. And what is still more curious, it gives some of our difficult sounds better than Mr. Faber himself can pronounce them. The ‘th,’ for instance, which is the Rubicon in our language to a German, it gives like a native-born American. Indeed, we do not believe the ‘Native American Party’ itself could tell the difference. On asking Mr. Faber how it came to pass his machine could speak better English than German, he replied: “Why shouldn’t it? –it is American born.” The sounds issue from the lips of a Mask that as they open and shut reveal a tongue that plays like the living member, though no so ‘limberly.’ It is really laughable to see this bust placed upright with a turbaned head and whiskered face slowly enunciating in a whining tone, sounds which we have heretofore considered as belonging exclusively to our species.” –New York Daily Tribune January 26, 1844.
In December 1845, Joseph Faber exhibited his “Wonderful Talking Machine” at the Musical Fund Hall in Philadelphia and Princeton University professor Joseph Henry (1797-1878) was called on to help determine whether or not Faber’s invention was a fraud. Henry soon became one of Faber’s chief supporters.
Barnum saw Faber’s demonstration in 1844 while in London and later arranged for Faber’s nephew to perform with Euphonia at Barnum’s museum in New York City. Prof. Faber had unfortunately committed suicide in 1850.
See more: http://history-computer.com/Dreamers/Faber.html
James Lastra, Sound Technology and the American Cinema: perception, representation, modernity (New York: Columbia University Press, c2000). Firestone Library (F) PN1995.7 .L37 2000