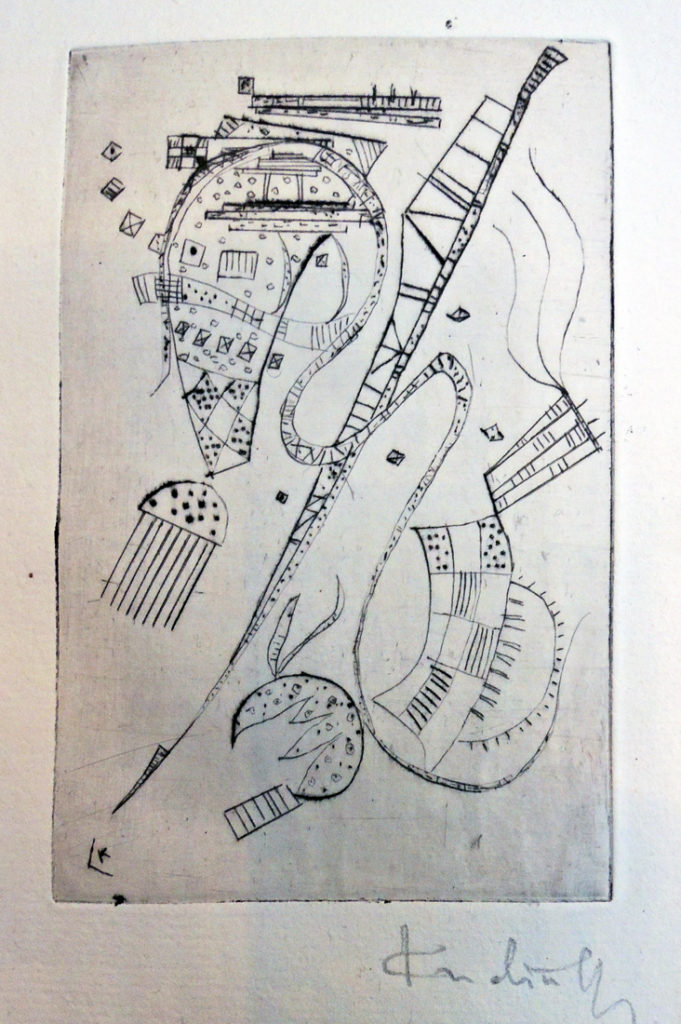
In 1927, the Curwen Press, Plaistow, partnered with Faber & Gwyer in London to publish a series called The Ariel Poems. Most are four pages with a previously unpublished poem and new printed image from a contemporary artist. No author was involved in the selection of the art and the final booklet (or keepsake) sold for one shilling.


“In his attempt to persuade eminent poets to contribute an Ariel poem, Richard de la Mare was not shy at telling poets that his father, Walter, had agreed to participate. In any case, he had come to know the older poets concerned through his father: in the displayed draft of a letter to Sir Henry Newbolt, for example, he writes that ‘Daddy has promised to let me have a new poem and so has T. S. Eliot’. In 1927, moreover, several of the writers when replying make polite enquiries about how his father was recovering from a recent illness. Rudyard Kipling was not able to help, but ‘A. E’ and W. B. Yeats were, and many other important literary figures came up with short poems for the sequence.”– https://www.faber.co.uk/blog/the-ariel-poems-numbers-1-8/

“Artists enjoyed the opportunity to work for the Curwen Press, not only for fees paid but because of the care taken reproducing their work. This was particularly true of illustrations reproduced by the pochoir (stencil) process, set up by Harold Curwen in 1925 and continued until 1932. The process was exploited with great skill by E. McKnight Kauffer, but even he acknowledged how much his book illustrations reproduced by pochoir owed their quality to Harold Curwen’s skill in running a department for which he trained the staff so well.” —http://whittingtonpressshop.com/the-curwen-press-collection-in-cambridge-university-library/
Between 1927 and 1931 Faber published thirty-eight poems in the Ariel series and then, in the early 1950s, after a gap of twenty years, it was decided to revive the series. Princeton University Library has a number of these, although not a complete set, spread out between a number of collections.
1. Yuletide in a younger world by Thomas Hardy, drawings by Albert Rutherston (London: Faber & Gwyer, 1927).
2. The linnet’s nest by Henry John Newbolt, drawings by Ralph Keene (London: Faber & Gwyer, 1927).
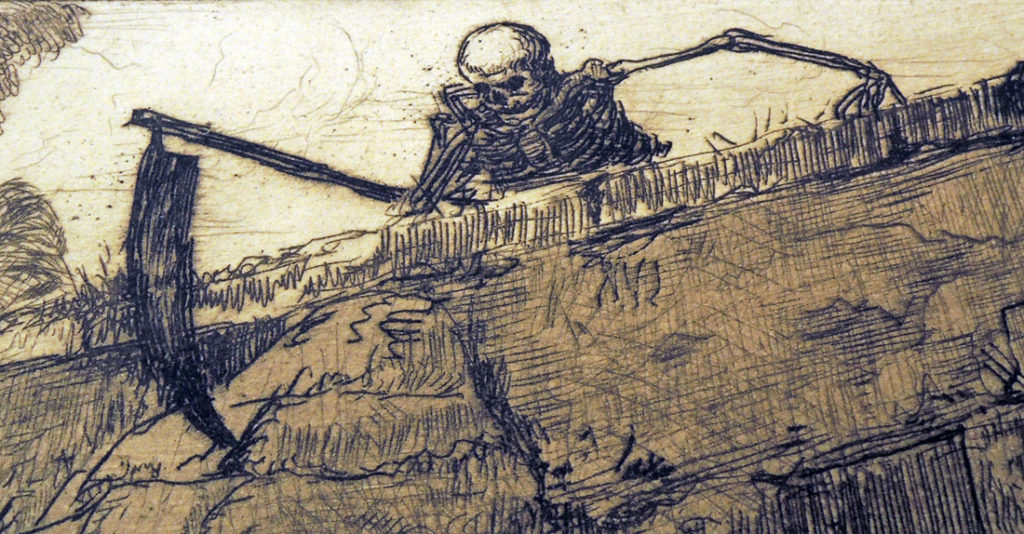
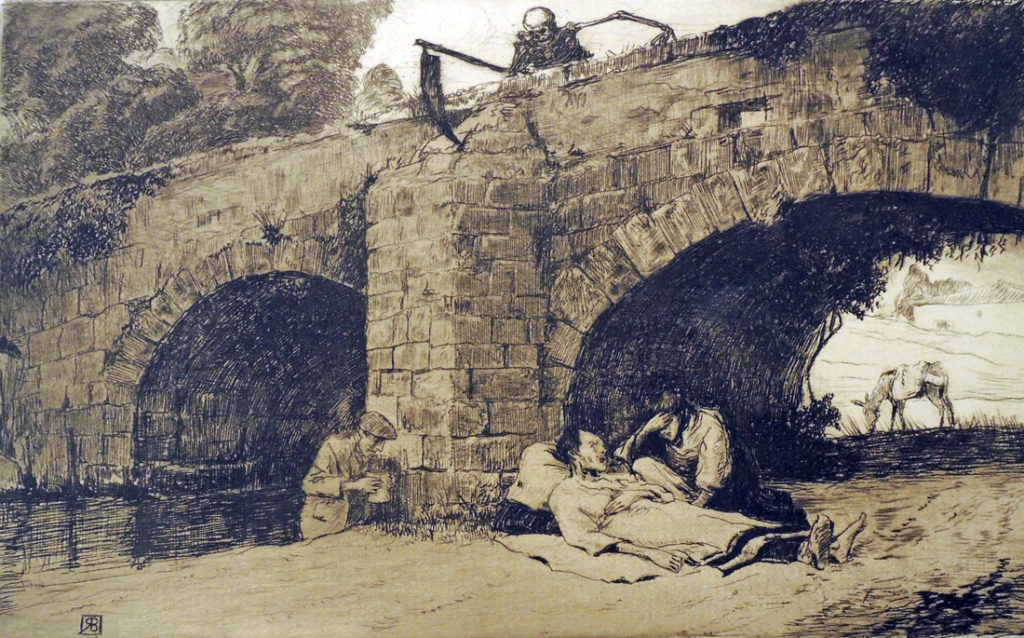
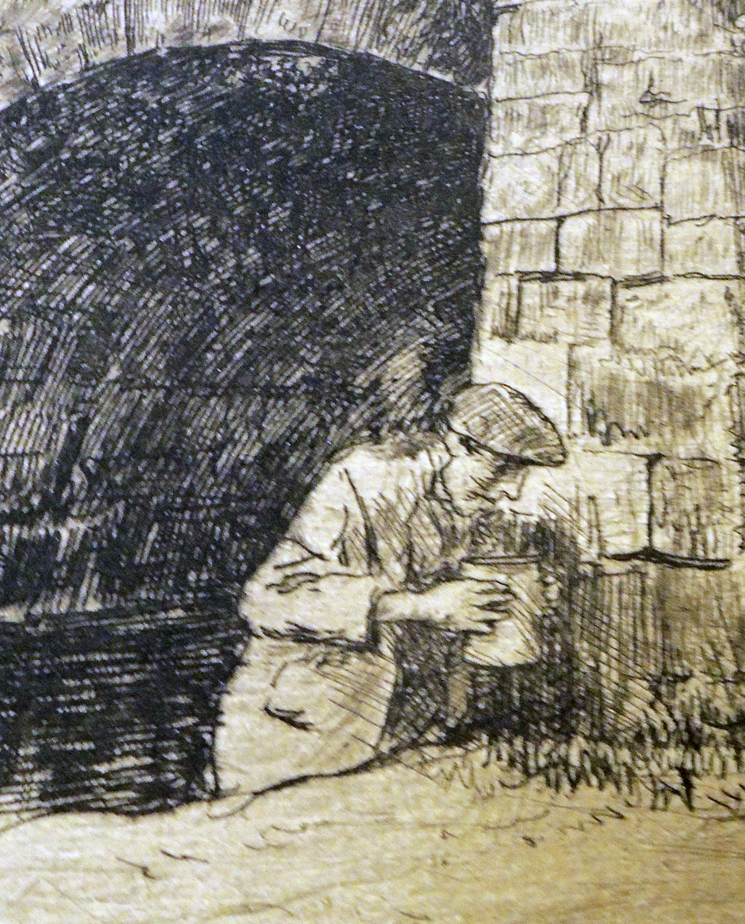
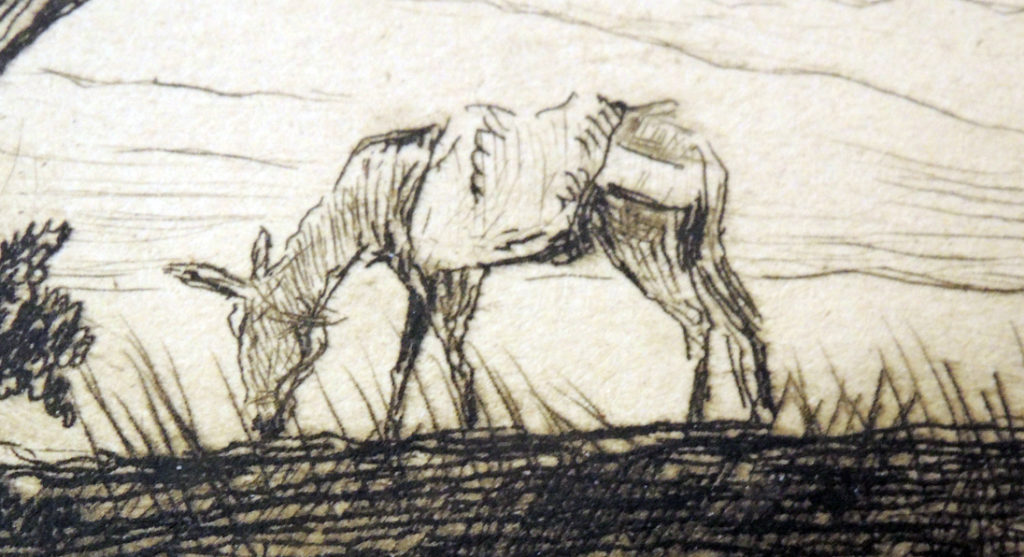
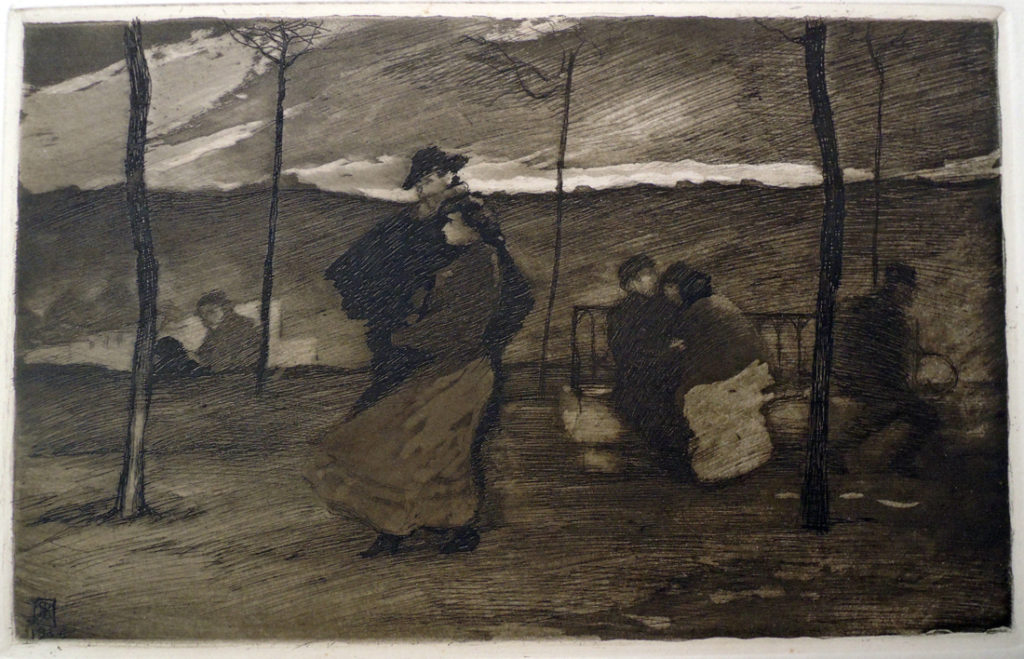
3.The wonder night by Laurence Binyon; drawings by Barnett Freedman (London: Faber & Gwyer, [1927]). 350 copies. ReCAP 3628.5.398
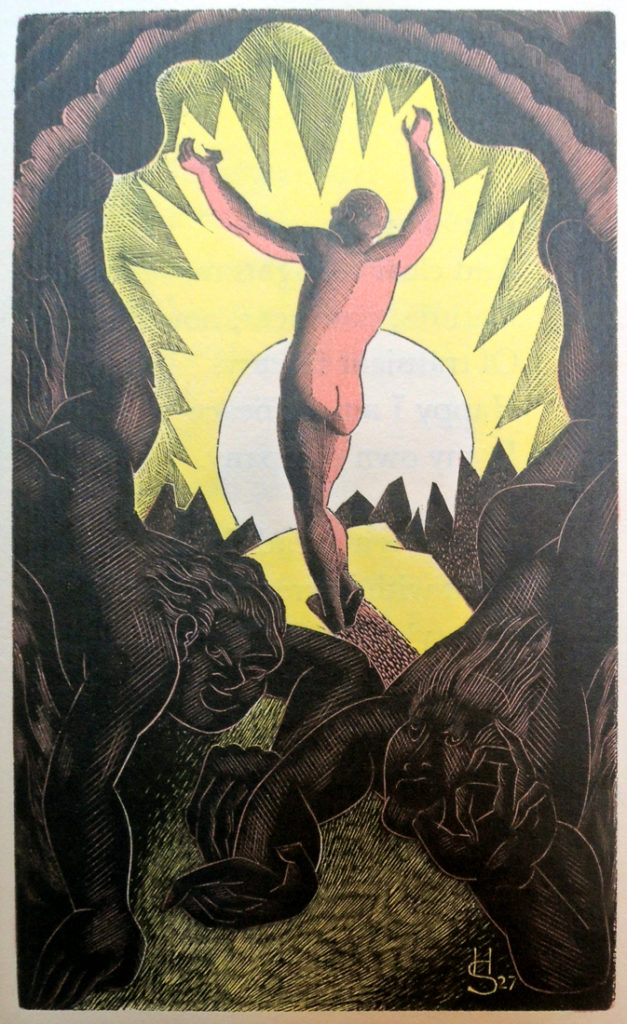
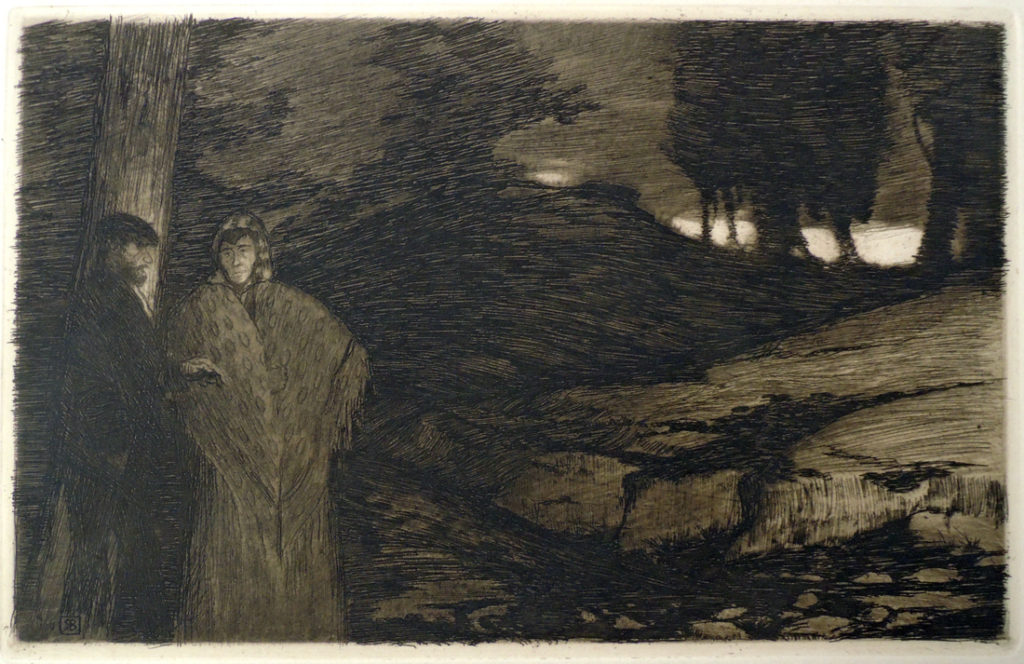
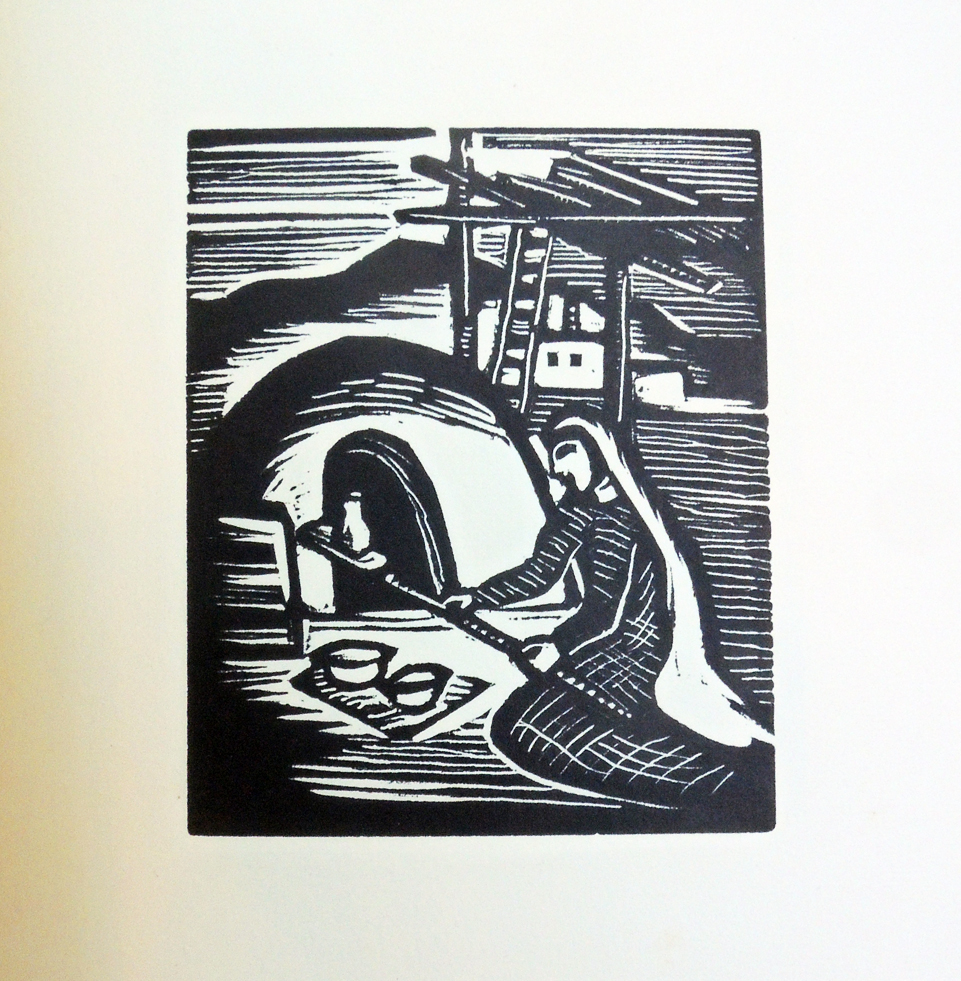
4.Alone by Walter de la Mare; wood engravings by Blair Hughes-Stanton (London: Faber & Gwyer, [19–?]). No. 68 of 350. Rare Books PR6007.E3 Z99046
5.Gloria in profundis by G. K. Chesterton; wood engravings by Eric Gill ([London, Faber & Gwyer, 1927]). No. 185 of 350. Rare Books 3675.85.339
6.The early whistler by Wilfrid Wilson Gibson; drawings by John Nash ([London: Faber & Gwyer, 1927]). ReCAP 3752.3.331
7.Nativity by Siegfried Sassoon; designs by Paul Nash ([London: Faber & Gwyer, 1927]. No. 18 of 350. ReCAP 3917.75.367
8.Journey of the magi by T.S. Eliot; drawings by E. McKnight Kauffer ([London; Faber & Gwyer, Limited, 1927]). Graphic Arts Collection 2004-4195N
9. The chanty of the Nona by Hilaire Belloc, drawings by Hilaire Belloc (London: Faber & Gwyer,
1928).
11.Self to self by Walter De la Mare, drawings by Blair Hughes-Stanton (London: Faber & Gwyer, Curwen Press, 1928).
12. Troy by Humbert Wolfe ; drawings by C. Ricketts (London : Faber & Gwyer, [1928]). ReCAP 3995.18.391
13. The winter solstice, by Harold Monro; drawings by David Jones (London, Faber & Gwyer, 1928?). Rare Books 3862.62.397
14. To my mother by Siegfried Sassoon, drawings by Stephen Tennant (London: Faber & Faber, 1928). Rare Books 3917.75.349.1928
15.Popular song by Edith Sitwell, drawings by Edward Bawden (London: Faber and Faber, 1928). Rare Books 3933.05.373
16.A song for Simeon by T.S. Eliot; drawing by E. McKnight Kauffer (London: Faber & Gwyer, 1928). Graphic Arts Collection 2004-4218N
18. Three things, by W.B. Yeats; drawings by Gilbert Spencer ([London, Faber & Faber limited, 1929]). Rare Books 3999.4.3895.11
20.A snowdrop by Walter De la Mare; drawings by Claudia Guercio (London: Faber & Faber,
192?). Rare Books PR6007.E3 Z99047
22. The outcast by James Stephens; drawings by Althea Willoughby ([London : Faber & Faber, 1929 ). Rare Books 3943.35.369
24. Inscription on a fountain-head by Peter Quennell ; drawings by Albert Rutherston (London : Faber & Faber, [1929]). Rare Books 3902.17.349
26. Elm angel by Harold Monro,. Wood engravings by Eric Ravilious (London, Faber & Faber, 1930). Rare Books 3862.62.332
27.In Sicily by Siegfried, drawings by Stephen Tennant ([London] : [Faber & Faber], 1927). ReCAP PR6037.A86 I575 1930
29.Marina by T.S. Eliot; drawings by E. McKnight Kauffer (London: Faber & Faber, 192?). RHT 20th-125
30.The gum trees by Roy Campbell ; drawings by David Jones (London : Faber & Faber, 1930). Rare Books 3664.55.341
31.News by Walter de la Mare ; drawings by Barnett Freedman (London: Faber & Faber, 1930).
Firestone Library PR6007.E3 N497 1930
33. To Lucy by Walter de la Mare ; drawings by Albert Rutherston (London : Faber & Faber, [19–?]). Rare Books PR6007.E3 Z99059
34. To the red rose by Siegfried Sassoon ; illustration by Stephen Tennant (London : Faber & Faber, [1931?]). Rare Books 3917.75.391
35. Triumphal march by T.S. Eliot ; drawings by E. McKnight Kauffer ([London : Faber & Faber, 1931]). RHT 20th-132
36. Jane Barston, 1719-1746 by Edith Sitwell ; drawings by R. A. Davies (London : Faber & Faber, [1931]). Rare Books PR6037.I8 J36 1931
38. Choosing a mast / by Roy Campbell ; drawings by Barnett Freedman (London : Faber & Faber, 1931). Rare Books 3664.55.325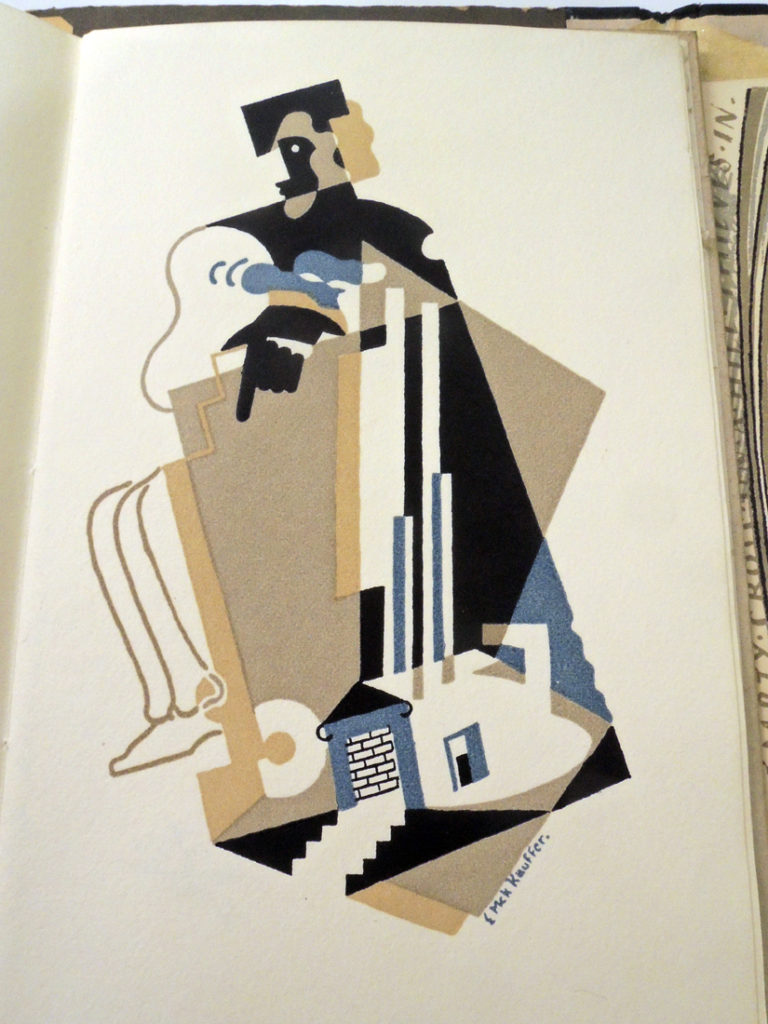
 For those not on the Platesblocksstones list, see here the information from Ad Stijnman about these beautiful 16th century woodblocks.
For those not on the Platesblocksstones list, see here the information from Ad Stijnman about these beautiful 16th century woodblocks.